Comparison between company and sole trader profits, to ascertain which business structure is more tax efficient
Comparison between company and sole trader profits, to ascertain which business structure is more tax efficient
Dated 13th March 2017
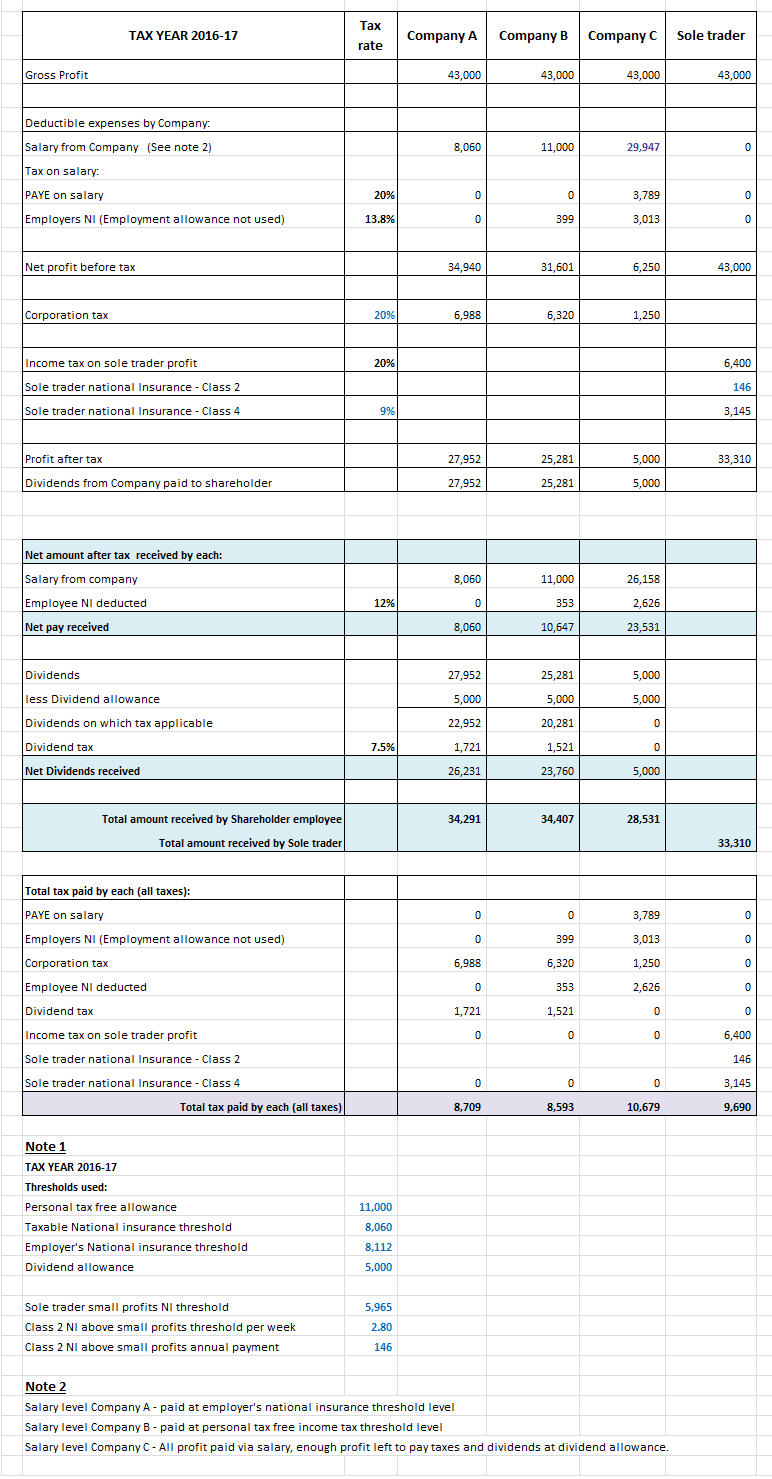
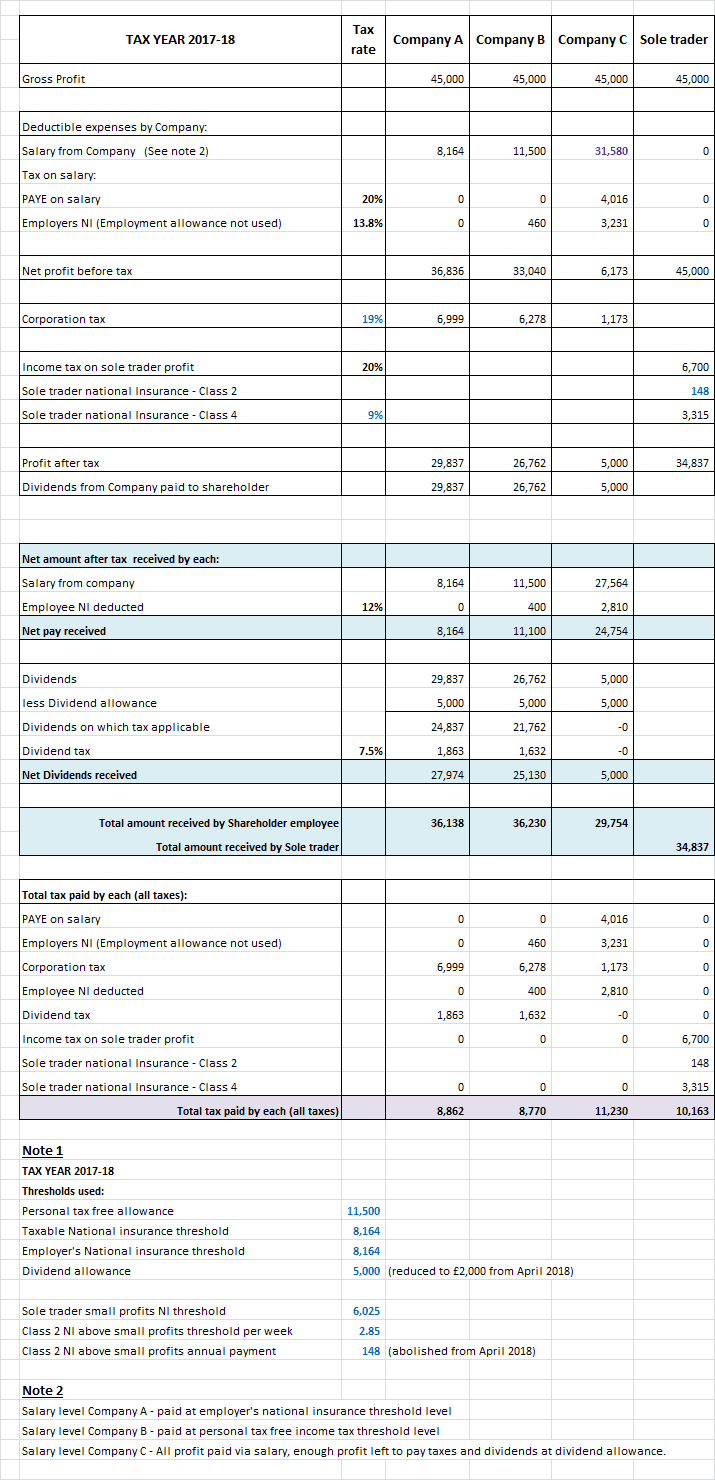
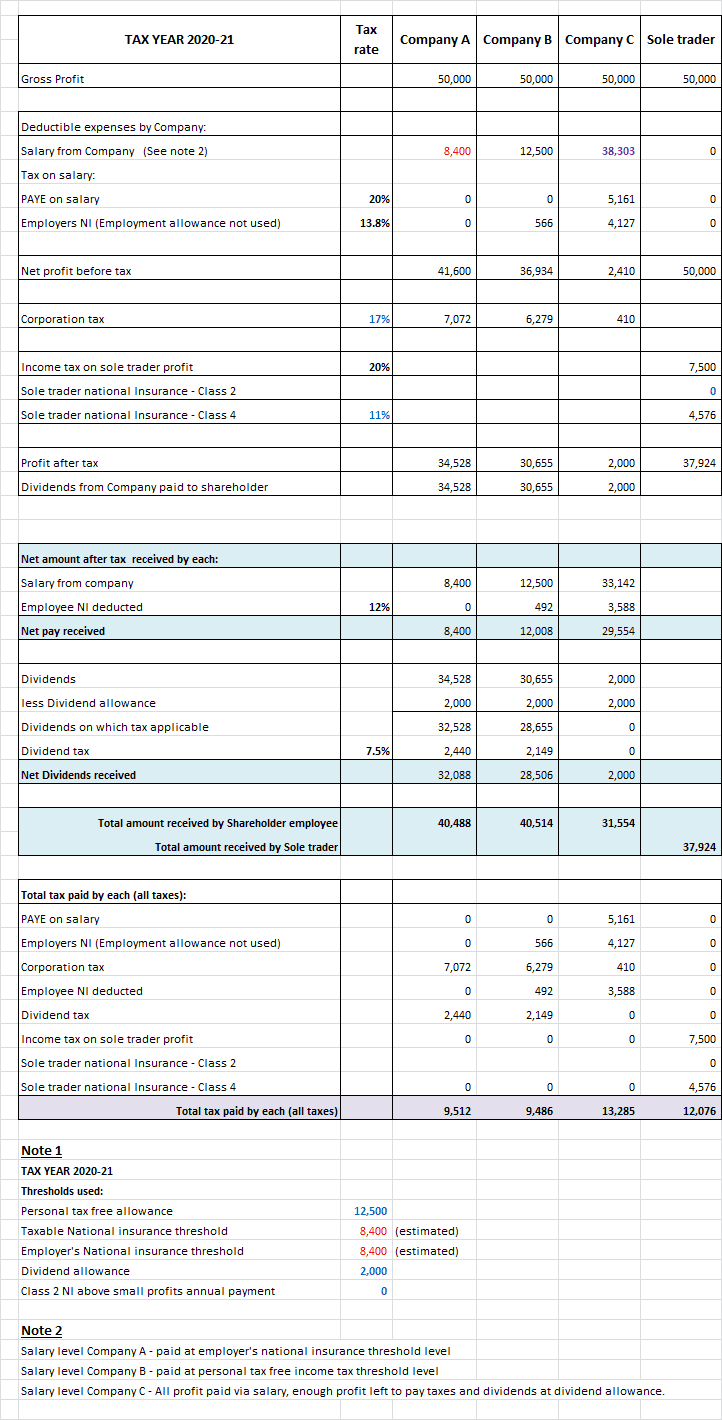
The table below covers tax years 2016-17, 2017-18 and 2020-21. Significant changes were announced in 2016 and in March 2017 to taxes related to a limited company and national insurance increase for sole traders i.e. self -employed.
The scenarios below is for a one shareholder/director who is the sole employee of the company. The gross profit is restricted to basic rate threshold level in that tax year.
Company A strategy - the shareholder/employee pays themselves minimum salary and all profits after corporation tax are paid to them as dividends.
Company B strategy - the shareholder/employee pays themselves up to the income tax tax free allowance each year, thus incurs a small employer national insurance. This is because employment allowance is not available to single shareholder/director companies.
All profits after corporation tax are paid in dividends.
Company C strategy - the shareholder/employee pays themselves maximum salary possible from the profit of the company. There is enough room left in the profit to pay for PAYE and NI. Profit after corporation tax is just enough to pay the minimum amount of dividends that is tax free.
The last row in blue shows the net amount (of the gross profit) received by the business owner after taxes.
The last row in purple sums up the total tax paid. You will note that operating via a private limited company is still more tax efficient. (don't forget all other advantages of operating via a limited company).
Follow Us
The information contained in this site is provided for information purposes only and is of a general nature. It is not a substitute for specific professional advice in your own circumstances. You are recommended to obtain specific professional advice from a professional accountant or tax specialist before you take any action. Whilst we endeavour to use reasonable efforts to furnish accurate, complete, reliable,error free and up-to-date information, we do not warrant that it is such. We and our suppliers disclaim all warranties. By providing information on this website we do not create an accountant-client relationship. This website is published for the information of clients and prospective clients. The information can only provide an overview of the regulations in force at the date of publication, and no action should be taken without consulting the detailed legislation or seeking professional advice. Therefore no responsibility for loss occasioned by any person acting or refraining from action as a result of the material can be accepted by the authors or the firm.
Best Tax Services Ltd is registered in England, Registration no. 11686758, Registered office The Hub, 20 Dawes Road, Fulham, London SW6 7EN
